How to update these docs
This documentation is intended to editable and updated regularly by the Seshat team. This includes any researcher, developer/admin, project manager or project lead working on the Seshat Global History Databank. If you are on the Seshat project, you can contribute to these docs by following the steps below.
When and why to update these docs
The main purpose of these docs are to ensure that the methods and processes of researchers and developers are well documented and easy to follow, which is helpful for both new and existing team members.
You should update these docs if:
You have particular method, process or way of working that you’d like to share with the team (or be able to repeat yourself in the future).
You have noticed that a particular section of the docs is out of date, incorrect or has important details missing.
How to request an update to these docs
If the documentation update you’d like to make is best handled by someone else, such as one of the Seshat Databank Admins, create a new issue on the Seshat repository.
Choose the “Documentation Improvement” issue template and provide as much detail as possible about the update you’d like to make.
Once the issue is created, you may wish to add a specific person under the “Assignees” section, or leave it blank if you’re happy for anyone to pick it up.
How to update these docs yourself
In order to update these documentation pages, first you’ll need to ensure you are set up with an account on GitHub and have Git, Python and Anaconda installed on your computer.
If you lack any of these, follow the steps on the Software tools page to get set up.
Once you have these pre-requisites, you can follow the steps below to update the documentation:
Fork the Seshat repository to your own GitHub account, by clicking the “Fork” button in the top right of the repository page.
Note: if you have done this before, go straight to your forked repository and click the “Sync fork” button to ensure you have the latest changes from the original repository.
If you haven’t already, clone your forked repository to your local machine.
Open Terminal (Mac/Linux) or Anaconda Command Prompt (Windows) and navigate to the directory where you want to store the repository.
Type the following command to clone the repository, replacing <your_github_handle> with your GitHub username:
git clone https://github.com/<your_github_handle>/seshat.git
Create a new branch for your changes.
Navigate to the repository directory on your local machine and ensure the dev branch is up to date.
cd seshat git checkout dev git pull
Create a new branch, with a descriptive name for the changes you are making.
git checkout -b <branch_name>
Make your changes to the appropriate documentation page(s) in the docs/source directory.
The pages are written in “reStructuredText” format. This is a simple markup language that is easy to learn and use. You can find a guide to the syntax here.
If adding new pages, ensure they are added to the “toctree” at the top of the index.rst file present in the same directory.
[Optional] Build the documentation locally to check that your changes are rendering correctly. Note: when opening a pull request in the last step you will be able to see a preview of the changes on GitHub anyway, but this could be quicker if you have a lot of changes to check.
Install the required dependencies for building the documentation. You may wish to use a virtual environment to avoid conflicts with other Python packages.
conda create -n seshat-docs conda activate seshat-docs pip install -r docs/requirements.txt
Navigate to the docs directory and build the HTML version of the documentation.
cd docs make html
Open the docs/build/html/index.html file in your browser to view the updated documentation.
Use Git to stage and commit your changes.
Stage the changes you have made to the repository.
git add docs/source/<path_to_file>
Commit the changes with a descriptive message.
git commit -m "Add/update <page_name> in docs"
Push the changes to your forked repository on GitHub.
git push origin <branch_name>
Open a pull request on GitHub.
On GitHub, click “Pull requests” and then “New pull request”.
Set the head repository to your forked repository and the compare branch to the branch you have been working on.
Set the base repository to Seshat-Global-History-Databank/seshat and the base branch to dev.
Click “Create pull request” and add a descriptive title and description to the pull request.
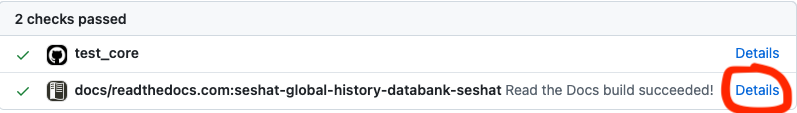
The documentation will be built automatically and you will be able to see a preview of the changes on the pull request page. Click “Details”.
A Seshat Databank Admin will review your changes and may request further changes before merging the pull request.
Once your pull request is merged, the changes will take a few moments before being reflected on this website.